Metabolic bone disease is generally known to be the type of disorder that affects the structure or strength of bone. Osteoporosis is the common widespread of these conditions, yet various other metabolic bone disease types can result in abnormal functioning, fractures, deformity if not treated immediately.
Moreover, these disorders might be the consequence of genetic conditions, diet, lifestyle, or other latent disease conditions.
What Is Metabolic Bone Disease?
Metabolic bone disease can also refer to bone strength disorders generally caused by mineral abnormalities (like calcium or phosphorus), vitamin D, bone structure/mass, and Osteoporosis being the most widely recognized.
Although bone loss does happen as part of the typical maturing process, numerous diseases, medications, and conditions can lead to a higher risk of bone breakdown.
Regrettably, when the disorders are left untreated, Osteoporosis can result in delicacy fractures, bone deformities, and complicated disability.
Meanwhile, parathyroid gland problems additionally can causes bone disorders in some cases. There are few glands found in the neck which yield parathyroid hormone (PTH). The work of PTH is to ensure calcium and phosphorus are regulated in the blood.
Additionally, the PTH help with muscle function, enzyme synthesis, and blood clotting. There are various kinds of parathyroid disease, which as to be typically tertiary, secondary, or primary. These can include diagnosis by physicians while treatments are administered where appropriate.
Metabolic Bone Disease Types
Metabolic bone disease refers to any disease that causes different bone abnormalities or deformities. There are different types of metabolic bone disease, including;
- Osteoporosis
- Fibrous Dysplasia
- Paget’s disease of bone
- Osteomalacia (or rickets)
- Renal Osteodystrophy
- Parathyroid Disorders
- Disorders of Mineral Metabolism
- Chemotherapy-Induced Bone Loss
In medical terms, metabolic bone disease may bring about pain in the bone. This can also begin to loss of height as a result of vertebrae compression. Subsequently, these makes predispose patients to fractures.
Metabolic Bone Disease: Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a well-known metabolic bone disease characterized by expanding bone loss that can result in fractures, loss of height, and kyphoscoliosis, which has an appearance with curved and bump back.
Moreover, Osteoporotic bones are powerless because it doesn’t generally need a tumble to cause injury.
Consequently, the bending over can be of the means that triggered the fracture compression experienced in the Spinal.
Osteoporosis Causes
In adolescence and early adulthood, bone loss results from a failure to accomplish apex bone mineral density, and accelerated bone loss might be specially noted around menopause and later years.
Numerous components, including diet and the absence of appropriate exercise, add to bone loss during these periods. It can likewise happen because of various underlying conditions, numerous of which are regularly not readily evident during the course of a doctor visit.
Furthermore, individuals who are at the highest risk of developing Osteoporosis are post-menopausal women. Other factors that affect Osteoporosis’s affected patients are poor nutrition, excessive alcohol consumption, heredity, usage of steroids, smoking, fair complexion, and a sedentary lifestyle.
How To Diagnose Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is the most well-known metabolic bone disease where there is a breakdown in the bone tissue, making bone progressively sensitive, leading to expanding risk of fracture. It is a “quiet disease” since there are no apparent signs or manifestations until fractures happen.
Osteoporosis can be diagnosed by carrying out a DXA bone mineral density test. This will assist the doctor with determining whether the disease is Osteoporosis. Moreover, blood, as well as urine test, will also help to reveal the underlying conditions and medical requirements.
Osteoporosis – Metabolic Bone Disease Treatment
Osteoporosis treatment requires the prescription of unique medications to ensure an increase in the mineral density of the bone. This involves a lifestyle that helps prevent Osteoporosis, like eating a healthy diet, taking supplements of calcium and vitamin D, and risky conduct limitation.
The main objective is to ensure that the risk of fracture is reduced. However, your doctor will clarify the risks and advantages of the different medications prescribed and work with you on selecting what’s suitable.
The treatment of Osteoporosis is conceivable by the prevention of further bone loss by managing the diet and enhancing it with calcium and vitamin D.
Osteoporosis Prevention
Numerous studies have revealed that calcium and vitamin D is a fundamental supplement for bone health. As part of daily routine, roughly 10,000 milligrams of calcium move through the skeleton to carry out bone renewal and repair.
Additionally, the measure of calcium that people need depends. Yet, adults usually need around 1,200 to 1,500 milligrams every day, even though food is typically known as a source of calcium. In contrast, some individuals may need a form of supplements for calcium.
Other approaches to implement to prevent Osteoporosis include;
- Keeping a good healthy weight
- By exercising to help build bone and keep up healthy bone
- Stopping or avoiding smoking tobacco
- Reduction in alcohol consumption – two drinks a day builds the risk of fracture
Also Read: Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment: Can Arthritis Be Cured?
Metabolic Bone Disease: Fibrous dysplasia
Fibrous dysplasia is an exceptional metabolic bone disease where fibrous (scar-like) tissue grows instead of typical bone.
This unpredictable tissue can debilitate the bone that is affected and results in fracture or deformity.
Moreover, fibrous dysplasia happens at a particular site in one bone yet can happen at different areas in various bones. Notably, the involvement of a single bone ordinarily happens in youths and early stages of adulthood. Individuals who have more than one influenced bone regularly create symptoms before the age of 10.
Fibrous Dysplasia Metabolic Bone Disease Symptoms
Fibrous dysplasia may cause not many or no signs and symptoms, especially if the condition is gentle. More severe fibrous dysplasia may cause including Bone pain, a curvature of leg bones, typically a gentle to direct dull pain, bone deformity, swelling, bone fractures, especially in the arms or legs, etc.
Additionally, Fibrous dysplasia can influence any bone in the body. However, the most usually influenced bones incorporate are thighbone or femur, Shinbone (tibia), Upper arm bone (humerus), Skull, Ribs, and Pelvis.
Occasionally, fibrous dysplasia might be related to a syndrome that influences the hormone-creating glands of your endocrine framework. These abnormalities tend to occur in the early stage of puberty, Overactive hormone creation, and Light earthy-colored spots on the skin. Likewise, increased bone pain might be related to the typical hormonal changes of the feminine cycle or pregnancy.
Fibrous Dysplasia Causes
Fibrous dysplasia is related to a gene mutation found in specific cells that produce bone. Moreover, the mutation brings about the creation of immature and unusual bone tissue. Frequently, the unusual bone tissue or lesion is available at a particular site in one bone. Occasionally, this can make multiple bones be affected, and there might be numerous lesions on numerous bones.
Fibrous Dysplasia Diagnosis
The vital device for the diagnosis of fibrous dysplasia is an X-beam. While bone seems strong in an X-beam, a fibrous dysplasia injury has a particular overall appearance frequently portrayed as “ground glass.” Consequently, the condition might be analyzed even in an individual without any symptoms who are getting an X-beam for different reasons.
Other tests carried out to diagnose fibrous dysplasia include imaging tests, Bone scan, Biopsy, and some more!
Fibrous Dysplasia Metabolic Bone Disease Treatment
Notably, the medication for the treatment of Osteoporosis is called bisphosphonates. It helps prevent bone loss by diminishing the action of cells that regularly break up bone. Some researchers propose that bisphosphonates may enhance affected bones by fibrous dysplasia and may lessen bone pain.
Also Read: Benefits Of Bone Broth Powder From Intentionally Bare – A Healthy Superfood
Metabolic Bone Disease: Paget’s Disease
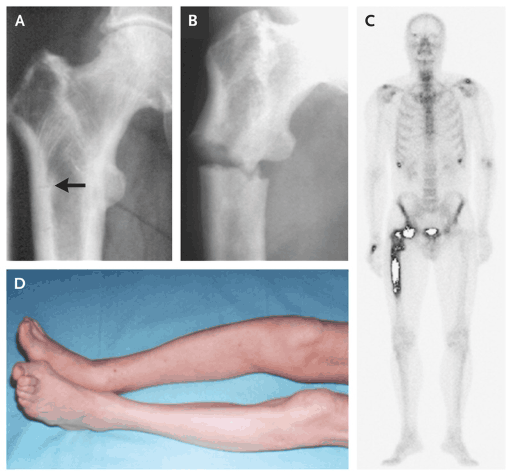
Paget’s disease is a type of metabolic bone disease known as a chronic disorder, making bones delicate and ineffective for ideal regeneration.
Individuals with Paget’s disease create new bone rapidly, yet the new bone is strangely tender and frail.
Meanwhile, individuals who suffer from this disorder regularly endure pain and weakness and are at higher risk of bone deformities, arthritis, and fractures.
Also, Paget’s disease symptoms are generally pronounced in the collar bone, spine, thigh, pelvis, or upper arm. However, some individuals additionally experience numbness, stiffness, or tingling in these body parts.
How to Diagnosis Paget’s Disease
Paget’s disease is typically referred to as the second most basic kind of metabolic bone disease following Osteoporosis. It is a complication of the bone remodeling measure, in which the body assimilates old bone and structures unusual new bone.
To diagnose if an individual has, a blood test known as alkaline phosphatase is carried out. Individuals with the disorder have an abundance of alkaline phosphatase (refer to an enzyme) in the blood.
Moreover, numerous diseases or conditions may be the reason for increased alkaline phosphatase levels in the blood.
Symptoms of Paget’s Disease
A person’s body with Paget’s disease may create new bone in inappropriate areas or remove old bone from its intended territories.
This can lead to deformities, bone weakness, bone pain, fractures, and arthritis. Numerous individuals with Paget’s disease do not understand that they have it. This is due are regularly either mild or undetectable symptoms.
If an individual with Paget’s disease fractures a bone, it might take a long effort for the healing process to conceivable due to the issues in the bone restoration measure.
Numerous individuals don’t know that they have Paget’s disease since they do not seem to have noticeable side effects.
This metabolic bone disease symptoms may likewise be confused with any other bone disorders, like arthritis.
The most widely recognized symptoms associated with Paget’s disease can occur or identify with bone or joint pain. Likewise, other common symptoms that can experience are tenderness, joint swelling, or redness of the skin that covers the affected area by Paget’s disease.
Meanwhile, some individuals get to know about the indication of Paget’s disease after encountering a fracture in a weakened bone.
Paget’s disease usually happens in the accompanying bones such as the spine, the pelvis, the skull, the tibia, the femur, or thighbone, or shin bone.
However, numerous primary nerves in the body go through, or alongside the bones, so unusual bone development may leads to compress or pinch or nerve damage, setting off the pain.
Paget’s Disease Treatment
Importantly, Paget’s disease treatment involved the use of medications which can be oral or injectable, anti-inflammatory drugs, and exceptionally manufactured footwear or orthotics. On account of seriously damaged bones, medical procedures may be required.
Notably, not all individuals with Paget’s disease often require treatment unless symptoms are apparent or if tests indicate that treatment is essential. Fundamentally, the top line of treatment will generally be bisphosphonates. Additionally, vitamin D, as well as calcium, might also be prescribed as supplements.
Bisphosphonates are medications that assist in limiting the breakdown of disordered bone. Individuals who were prescribed bisphosphonates additionally need to keep up adequate does of vitamin D and calcium.
Also Read: Self-Diagnosis Online Dangers And How To Avoid Them In 2021
Metabolic Bone Disease: Osteomalacia
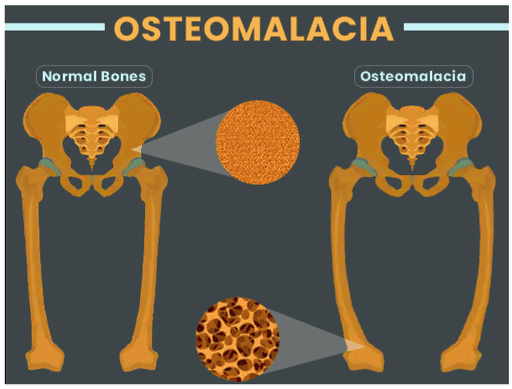
Osteomalacia, otherwise called rickets, is a disease of bone softening that occurs because of a severe vitamin D deficiency.
As such, this condition results in dull throbbing pain, muscle weakness, and a higher risk of fractures, particularly inside the spine, rip, and legs.
Osteomalacia Symptoms
Also, changes of diet for the long term are advised. Moreover, certain underlying conditions, including kidney failure, liver disorders (or disorders), may lead to difficulty in nutrient absorption, leading to Osteomalacia.
Furthermore, the treatment of these conditions can likewise assist relieve side effects. However, leg braces or surgery may be needed for other advanced cases of Osteomalacia.
Osteomalacia Treatment
The treatment for Osteomalacia is conceivable using vitamin D deficiency for correction by the usage of oral supplements or infusions.
Also Read: What Foods To Eat After Hernia Surgery And What Should Avoid?
Metabolic bone disease: Renal osteodystrophy
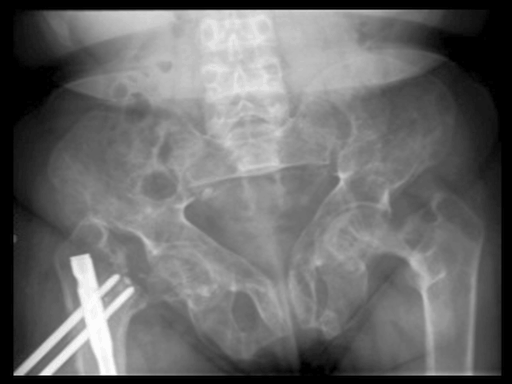
Renal osteodystrophy is also known as chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD).
Renal osteodystrophy occurs as a kidney dysfunction consequence.
When the kidneys are not functioning as expected, the body neglects to manage blood levels as appropriate for calcium and phosphorus; this leads to why the bones are affected.
Renal Osteodystrophy Causes
Moreover, CKD-MBD usually occurs in patients having kidney disease and a practicing general challenge for patients on dialysis. Since the condition lowers the growth of the bone and can result in deformities, CKD-MBD is generally a severe health challenge in children whose bones are just developing.
Renal osteodystrophy might be of usually short height and resulting in leg deformity called “renal rickets.” In adults, CKD-MBD can start influencing the bones a very long time before individuals experience the symptoms. This is why the disease has been referred to as a silent crippler.
However, CKD-MBD in adults left untreated can result in continuous thinning bones, bone & joint pain, and a higher risk of fracture.
Also Read: Benefits Of Healthy Blood Circulation In Your Body
Metabolic Bone Disease: Parathyroid Disorders
The parathyroid glands are found at the neck and are known to assist in managing calcium levels in the blood. On the contrary, parathyroid glands can make calcium levels in the blood get abnormal when the glands are malfunctioning.
Moreover, bone loss can occur due to either hyperparathyroidism or hypoparathyroidism if no treatment is administered. Likewise, this may result in bone fractures, spine curvature as well as height loss.
Parathyroid Disorders Treatment
Essentially, Hypoparathyroidism treatment is often associated with the administration of vital bone minerals like calcium and vitamins like vitamin D.
Further, the treatment of hyperparathyroidism is conceivable with medication and, regularly, might require surgical for the removal of affected glands.
Also Read: How To Get Healthy And Stay Healthy?
Metabolic Bone Disease: Disorders of Mineral Metabolism
The balance of minerals in the body is a sensitive one. It is essential because any deficiency or surplus of one substance frequently influencing one level or another.
Notably, when the body neglects to regulate a suitable balance of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium all alone, then administering a medical mediation is very important.
The incapable of the body to regulate minerals on its own can be due to an assortment of kidney, gastrointestinal, and bone conditions.
Metabolic Bone Disease: Chemotherapy-Induced Bone Loss
As a shocking result of the chemotherapy used to treat different malignancies, there is a possibility of patients being affected with bone loss.
Moreover, numerous medications, including bisphosphonates, are beneficial in forestalling or treating this severe side effect.
Featured Image by MART PRODUCTION from Pexels


Comments are closed.